While setting up an entity in India, foreign companies should choose an entity structure that caters best to their need. Selection of the right entity structure will help the company establish itself as a strong player in the Indian market and reap financial gains.
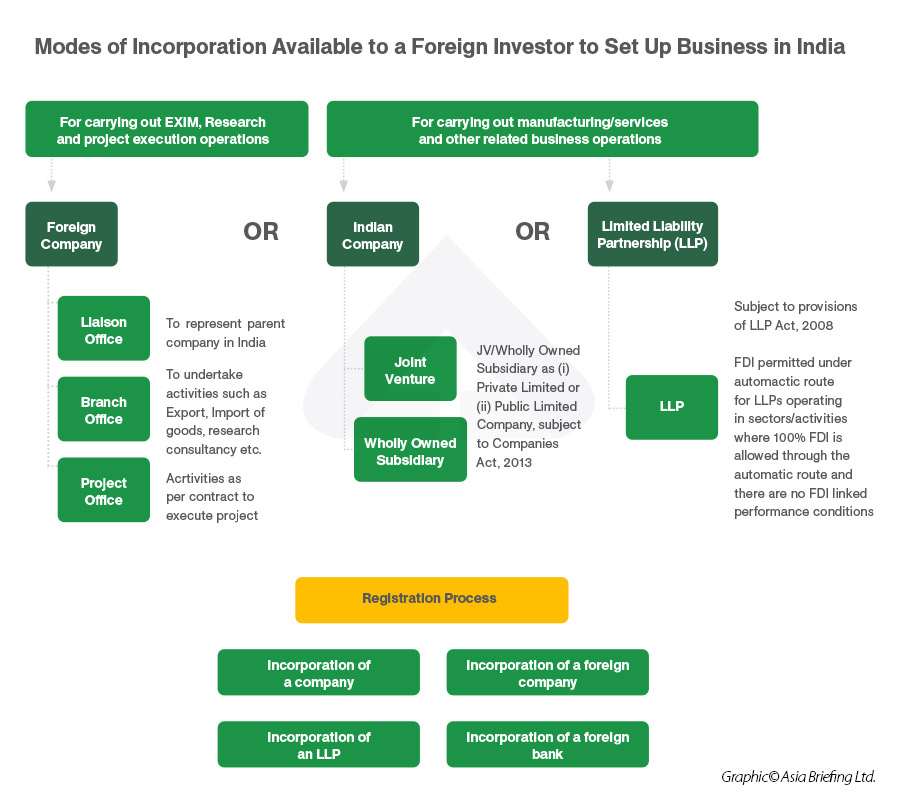
A foreign investor or company may be set up as an unincorporated entity or incorporated entity.
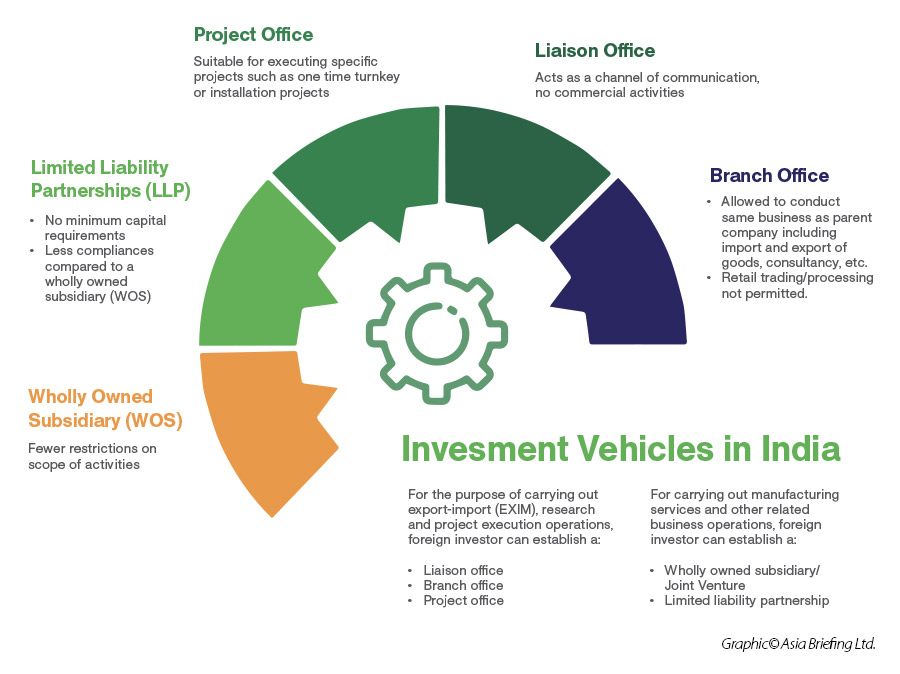
Unincorporated entities permit a foreign company to do business by establishing a liaison office, branch office, project office, or trust. An incorporated entity, like a limited liability partnership, joint venture, or wholly owned subsidiary, is considered a separate legal entity and has a more structured setup.
Choosing a corporate structure
Depending on the type of activity it intends to conduct, investors can start commercial operations by registering as either a foreign entity or an Indian entity.
Before choosing which type of company to establish, it is important to consifder different aspects of the target entity types, such as differences in structure, legal liability, statutory compliance requirements, the time required to establish it, what types of activities it can engage in, and more.
These considerations help identify the appropriate business constraints, costs, requirements, and risks necessary to enable the company’s future targeted capabilities, developments, and growth. The below links explain these factors for each of the main entity types that can be set up in India.
|
Key Market Entry Options |
||||
|
Entity Type |
Purpose |
Setup time |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Liaison Office (LO or Representative Office) |
|
6 - 8 weeks |
|
|
|
Branch Office (BO) |
|
6 - 8 weeks |
|
|
|
Project Office (PO) |
|
4 weeks |
|
|
|
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) |
|
4 - 6 weeks |
|
|
|
Wholly Owned Subsidiary (WOS) |
|
4 - 8 weeks |
|
|
For more details about any of these entity types, click on the structure type to read from our Types of Business in India guide section.
Requirements for setting up a business in India
|
Essential Processes and Compliances for Setting Business in India |
|
|
Setting up legal existence |
Obtain Director Identification Number (DIN) Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) for proposed Directors Approval for proposed Company/ LLP Name Finalization of supporting documents Filing of e-forms with CRC Verification of documents Consent to establish & operate Obtain Permanent Account Number (PAN) Registration for Tax Account Number (TAN) Registration of GST |
|
Registering and starting a unit |
Registering / categorization of units in the State Approval for State Incentives (Optional) IEM/EM Registration MSME Registration |
|
Pre-commissioning phase |
Acquisition of Land Environment, Forest, and Wildlife Clearance Permission for Land Use Pollution Board Industrial License Consent to Establish Factory Layout Plan Approval Registration of Boilers Building Plan Approval Registration under the Contract Labor Act 1970 Registration under BOCW Act Power for construction Provisional Fire Approval Approval for lifts and Escalator Environment, Forest, and Wildlife Clearance Permission for Land Use Pollution Board |
|
Post-commissioning phase |
Consent to operate Building Completion certificate Final Fire Approval Water Connection Power Authorization for hazardous waste Professional Tax Registration Central Excise Registration Shops & Establishment Act Employee Registration with ESIC Employer Registration with EPFO Trademark/ Brand Registration Importer Exporter Code (IEC) Customs- Special Valuation Branch Grant for Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) License Quality Marking Certificate |
Opening a bank account
Opening a bank account entails selecting a bank based on your preferences, submitting certain documents, and funding your account. Once the formalities are completed, you can begin using your account, saving both time and money. Companies are only permitted to create and operate current accounts; other features, such as fixed deposits, might be added at a later stage, depending on the needs of the firm.
The Reserve Bank of India’s Know Your Customer Norms (KYC Norms) details the procedures that banks must follow while opening accounts. With the KYC norms as a foundation to secure against fraudulent and criminal activities, each bank may require more documents and information as prescribed by the bank’s internal regulations for the opening of an account.
Intellectual property protection
India has been a World Trade Organisation (WTO) member since 1995. WTO member nations must include some IP protection in their national laws. India is also a signatory to the following international IP agreements:
- Paris Convention: Under this convention, any person from a signatory state can apply for a patent or trademark in any other signatory state and will be given the same enforcement rights and status as a national of that country.
- Berne Convention: Under this convention, each member state recognizes the copyright of authors from other member states in the same way as the copyright of its own nationals.
- Madrid Protocol: Under this convention, a person can file a single trademark application at their national office that will provide protection in multiple countries.
- Patent Cooperation Treaty: This is a central system for obtaining a ‘bundle’ of national patent applications in different jurisdictions through a single application.
The following laws provide the legal basis for intellectual property protections in India and are periodically reviewed and amended as new technological developments and market reforms necessitate the case to be.
Doing business without an entity
In India, businesses may do business without setting up a formal entity by working with a supplier agent or partner. On hiring an agent or supplier in India, businesses may conduct international trade through these partners.
Alternately, foreign companies may also use the “employer on record model,” wherein an India-based employer hires an employee on their payroll while the individual works for the foreign company. However, the foreign company takes on the risk of creating a permanent establishment in the country.
Closing a business in India
The liquidation procedure is governed by the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code. Businesses may opt for the liquidation procedure due to a set of factors, such as faulty management, economic issues, and low demand, among others. According to Indian legislation, the liquidation procedure refers to the way the company’s assets are terminated and distributed to the entitled parties. The liquidation can be triggered on a voluntary basis through the intervention of the company’s creditors or other members. In this case, the procedure can be completed without the intervention of a local court.