Recent news from China coupled with the Dezan Shira & Associates results in the year to date both show that foreign investment into both China and Asia overall continue to demonstrate strong rebound growth from the effects of Covid. At Dezan Shira, our overall results, as a firm handling foreign direct investment into Asia show positive results across the board, a point made by my colleague Dustin Daugherty from our US office in his editorial this week.
Elsewhere, data from the first two months of 2021 show that the already buoyant China-Europe rail routes, which had already doubled in 2020, expanded by a further 96% in January and February. A total of 2,213 freight trains were dispatched between cities in China and Europe in January and February combined, with some 209,000 TEUs dispatched along the routes, up 106% on 2020, according to reports from the China State Railway Group.
In terms of Foreign direct investment (FDI) into China in January-February, that jumped 31.5% to US$27.21 billion compared with a year earlier, China’s commerce ministry said on Friday. While it is easy to write that off as a rebound from last year’s position when lockdowns, and the severity of the pandemic was starting to become apparent, there are other fundamental issues at play.
I can describe the three major 2020 important policy changes that are now impacting foreign investors into China in 2021 as follows:
China’s New Foreign Investment Law
Changes to this had first been mooted back in 2015, with apparently competing versions of this doing the rounds between MOFCOM and the NDRC. President Xi then stepped in, and a draft was made ready by the end of 2018 and made available for public consultation. It was passed into law in Q1 2019, unusually fast for China, and took effect in January this year. Among many other provisions (we gave a background here and published a complete issue of China Briefing Magazine dedicated to the subject here) the new law opened China Government procurement tenders to foreign companies.
This is of relevance to the Belt & Road Initiative as many projects are quasi-sourced, or originate from China’s diplomatic channels, and almost immediately fall into the remit of their SOE’s. However, faced with challenges in certain constructions and other technological areas, and in need of the technology themselves, China allowed overseas partners to bid for projects. We discussed the implications of this in the article Understanding China’s New Foreign Investment Law as Concerns Belt & Road Procurement.
Change One:
Foreign companies can now bid for China Government Procurement Contracts.
China’s 2020 Amended Negative List
China’s ‘Negative List’ is a detailed description of which industrial and service sectors in China are open, partially open, or closed to foreign investors in China. The ‘Negative’ title reflects the off-limits sectors. The 2020 amendment significantly increases market access for foreign companies in China. We can see an example of the impact that has had in the following graphic concerning Germany, courtesy of China Investment Research and the Frankfurt School of Finance & Management.

Change Two:
Foreign investors have significantly improved China’s market access. While the EU may not wish to acknowledge this, that is largely in part because they are attempting to negotiate a free trade deal with China, and they do not wish to note that China already provided improved terms. Hence, the difference in EU negotiators stance that “more must the done to open up the China market” and Germany’s own corporate investors who have gone ahead anyway because the Negative List improved.
China’s ‘Dual Circulation Strategy’
This third development is squarely aimed at changing China’s economy from a producer economy to a consumer economy. It is State Policy and is being enacted. What it means is that China is looking to Chinese consumer’s domestic demand on one hand, while simultaneously developing conditions to facilitate foreign investment and boost production for exports on the other. The ‘dual’ nature of the concept refers to the parallel emphasis on an ‘internal circulation’ and an ‘international circulation’, and a shift towards becoming a demand and innovation-driven economy. We discussed this subject in the article What is China’s Dual Circulation Strategy and Why Foreign Investors Should Take Note.
The implications of this have not quite yet sunk in overseas. Chinese Finance Minister Wang Yi, addressing the Belt & Road Forum last week, stated quite expressly that: “This paradigm is aimed at promoting mutual openness and mutually reinforcing development between domestic and international circulations. It will fully unlock China’s market potential and facilitate greater opening-up. China has a population of 1.4 billion and a middle-income group exceeding 400 million. This year, the value of its domestic retail market will surpass US$6 trillion. In the coming decade, the total import of goods into China is estimated to top US$22 trillion.”
Change Three:
China is evolving rapidly to become a consumer-driven economy.
These three concurrent developments signify probably the strongest statement ever that China is open for business – and it wants to buy imported products. The implications of this for foreign investors and overseas export manufacturers could not be more crystal clear. Sell to China.
Changes to China’s Belt & Road Initiative Policy
China has also made changes, albeit rather more subtle, to how it intends to develop its ongoing Belt & Road Initiative policy. As I explained earlier, many of the initial projects are now coming to fruition, and there is simply not the need there was seven years ago to embark on massive supply chain builds. Instead, the following is taking shape:
How China companies are investing
China, in line with the BRI, remains a foreign investor in all the countries it has financed and established projects in. It also recognizes that in terms of operations, in many cases – it will be content to sit back with a minority position, take a seat on the board, and take dividends as a return on investment. In others, and especially those with major investments, it will continue with majority holdings but may later exit. The BRI projects China has invested in provide these choices.
We can examine how China has been building Tencent and Alibaba in this manner.
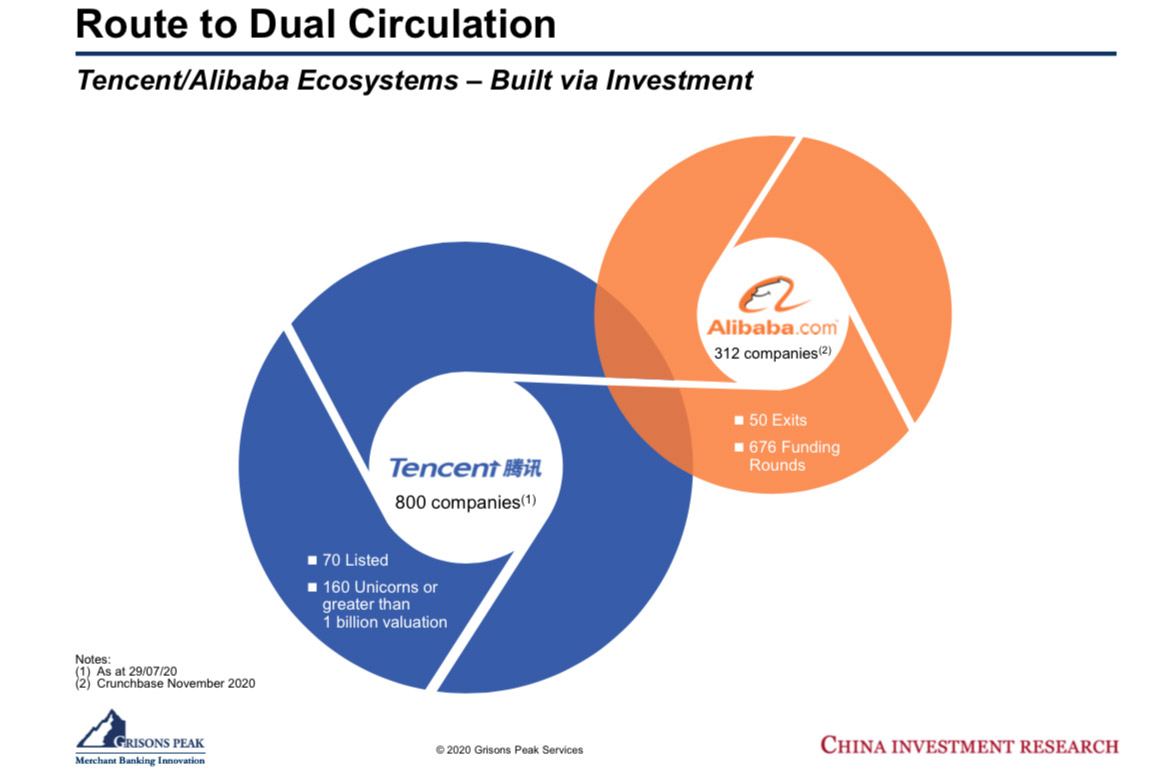
Tencent has invested in 800 companies, of which 160 are unicorns with a valuation in excess of US$1 billion, and 70 are listed. Alibaba has invested in 312, gone through 676 funding rounds, and made 50 exits. These are Chinese investors and growing their businesses in being such.
China IPOs 2020
This strategy is also showing up in the performance of Chinese IPOs. The three Greater China stock exchanges, Hong Kong, Shanghai, and Shenzhen accounted for 45 percent of total global IPOs between Q1 and Q3 in 2020. By mid-October, 308 Chinese companies had raised US$73.5 billion.
In the United States, 29 Chinese companies raised US$9 billion, and in the UK, two IPOs realized US$3.9 billion, all between Q1 and Q3 2020. It is a trend we can expect to see continue with major brands such as Liziyuan, a major national Chinese milk and beverage company, Zuming, one of China’s largest Soy Bean companies, Kuaishou, a mobile app provider and the China National Gold Group Gold Jewellery, all coming to markets in Hong Kong, Shenzhen and Hong Kong the past two months raising about S$5.6 billion. Other hot IPOs are coming this year too, with companies in China’s short video, food & beverage, biomedical, and precious metals sectors all coming to market.
Overseas funds
Increasing overseas funds are turning to hold Chinese sovereign debt, with 2020 showing an increase of US$66 billion in Q3 alone, the faster pace ever. Chinese securities have a 10-year yield of 3.9 percent, an attractive bet when US$16 trillion of global debt is yielding less than zero. Foreign institutional funds now hold nine percent of Chinese bonds, up from four percent in 2017.
Chinese overseas direct investment
Although several big-ticket BRI projects will continue to be funded in the coming years, China is taking a more strategic view – exiting investments to realize a set RoI, or building companies through investment. Increasingly, these take the form of strategically placed minority investments.
While the Financial Times might point out and suggest China ODI is slowing, which is correct, more research and less rhetoric might have shown them that China is now both concentrating on developing itself into a consumer-based economic model and that Belt & Road Initiative investments are being more strategically thought through
China’s Health Silk Road
An example here is China’s involvement in the Health Silk Road. China has exponentially increased its ODI investments in global healthcare, equity investments, and licensing during 2020. According to China Investment Research, China’s spending in Q3 2020 alone included 48 outbound investments in joint ventures and drug research for a July-September total of US$2.503 billion, with an average investment size of US$52 million. China’s acquisition or buying into overseas medical companies included businesses in Canada, Germany, Israel, Japan, Netherlands, Qatar, Singapore, South Korea, Switzerland, the UK, and the US.
It is a trend that will continue. China is putting its money where its mouth is in terms of partnering overseas in healthcare and this can be expected to be a major driver of future BRI and global healthcare development.
Summary
The policy changes I have pointed out are in place and are being acted on now. There is no doubt that China is very serious when it means it is open for business and that there are 400 million consumers it needs to have products delivered to. The changes COVID-19 has brought, especially in the digital arena, will further change the way in which tomorrow’s consumers will buy products – just look at how Amazon’s stock price and Jeff Bezo’s personal wealth have rocketed due to home deliveries this year.
China’s opening up – a new “Negative List” was issued last week, we explain the implications of that here – the easing of both China’s Foreign Investment Laws and the Dual Circulation Strategy are all combining to make China the consumer economy it wants to be. This is excellent news for manufacturers overseas – China wants your products. In China’s own ODI, this is being managed along with Chinese State Planning, and is slowing down from the heady days of multi-billion dollar infrastructure deals to more considered M&A. This represents a rather more mature China that is now emerging onto the world stage.
China still has money and is still making money. The three China bourses raised nearly half of the global money raised – outstripping the US as institutional investors raising capital for new businesses and developing them. China’s innovations are now being determined by the type of businesses that people are prepared to part with money for – and increasingly, almost exclusively, they are in hi-tech.
The way to China is to sell via hi-tech means going digital and online. We examined how to do that here.
Alternatively, foreign investors can establish operations in China, and sell directly from there – as well as export duty-free to markets in ASEAN and RCEP and elsewhere. We examined the manufacturing and trading establishment options for China here.
Or, if China costs are not quite your thing, you can do the same from ASEAN and sell to China from there – again that Free Trade Agreement applies. Our complimentary 2021 Guide to Doing Business in ASEAN can be downloaded here.
This is all occurring just at the same time that China is exiting its Belt & Road Initiative, or at least the major infrastructure part. There, too, are opportunities. China built Sri Lanka’s Hambantota Port, Airport, Free Trade Zone, and the road and rail infrastructure. It has now invested another US$300 million to set up a tire manufacturing facility utilizing those exact same facilities. Sri Lanka provided a tax sweetener just as China used to do for foreign investors back in the mid-1990s. China’s investment though will boost the local rubber industry, will, directly and indirectly, employ thousands, gives Sri Lanka technology access, and helps move forward the island nation’s desire to be a regional Asian tire manufacturer. You can bet that other BRI investments will also be used as springboards for Chinese companies. I discussed how non-Chinese companies can take advantage of China’s Belt & Road build here.
That BRI build completion means opportunities for local investors – exploiting the infrastructure. With over 3,000 Chinese-funded projects coming to fruition there is a lot to look at. We explored some of the key Eurasian hubs along the China-Europe rail freight routes here, some of the European BRI projects to watch here, and other developments in ASEAN here, South America here, and Africa here. We even discussed how US investors can take advantage of Central America’s BRI projects now coming to completion, while not leaving out our Russian friends either.
As you can see, there are plenty of options, and what China has accomplished in 2020 for 2021 foreign investors is just that – increased foreign investor options, and increased the available scope for involvement, investment, and returns on that. China’s future in 2021 is here, and it is looking increasingly profitable.
Have a great week ahead!
Stay safe
Best regards;
Chris Devonshire-Ellis
Chairman, Dezan Shira & Associates
Publisher, Asia Briefing
E: editor@asiabriefing.com
W: www.dezshira.com
Disclaimer
Any views or opinions represented in this blog are personal commentary, belong solely to the contributor and do not necessarily represent the views of Asia Briefing Limited or Dezan Shira & Associates.


